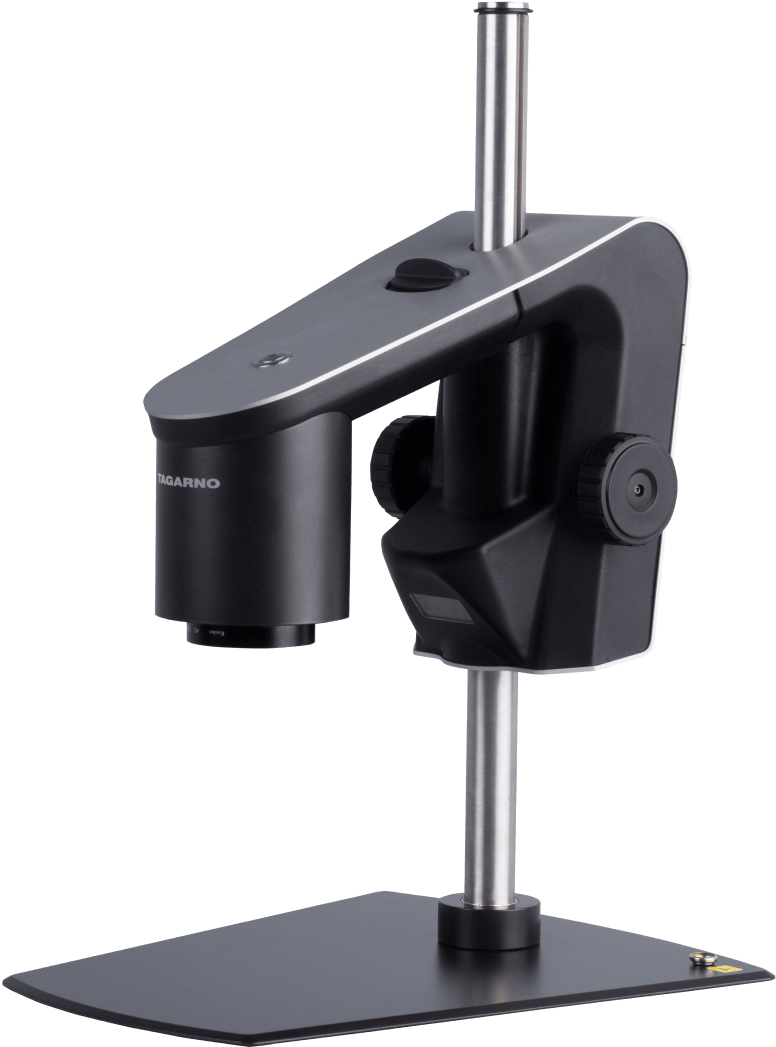
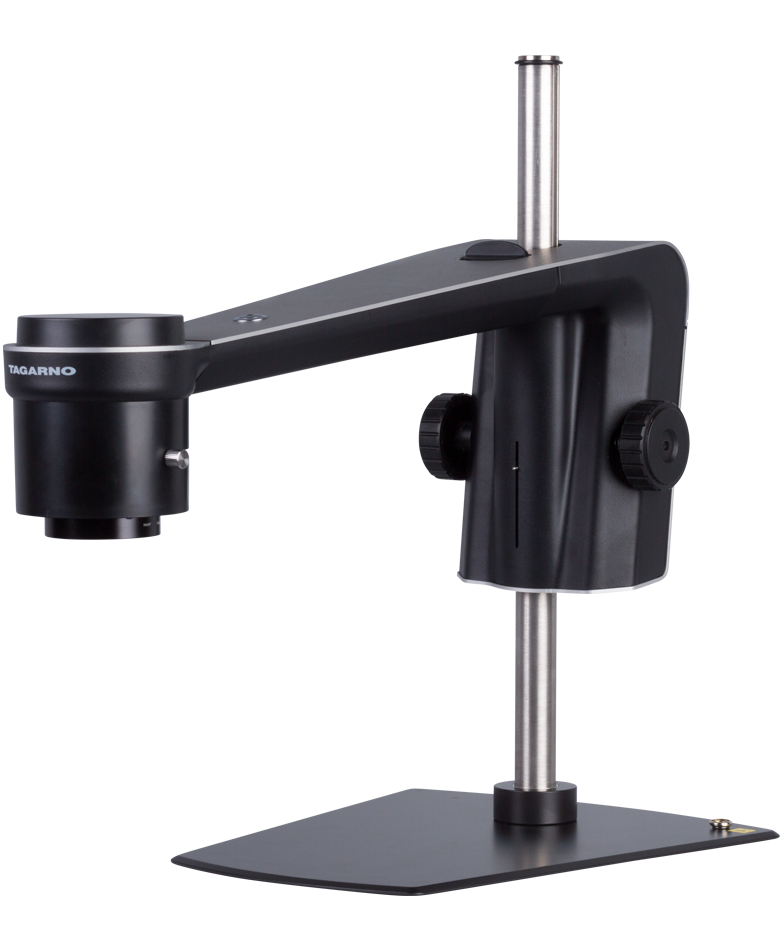
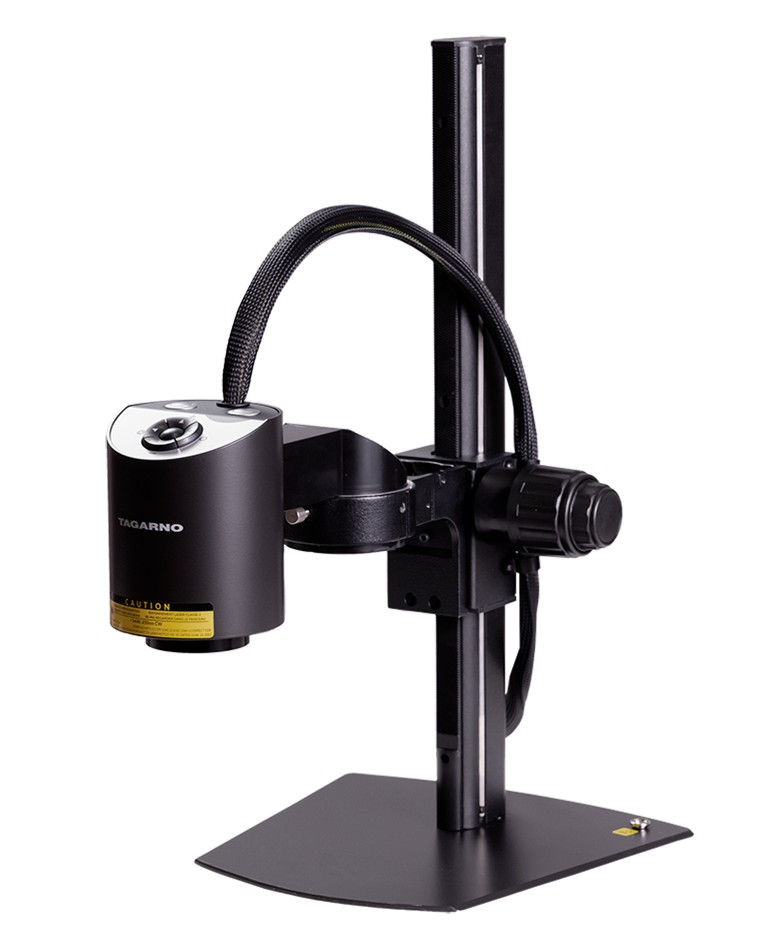
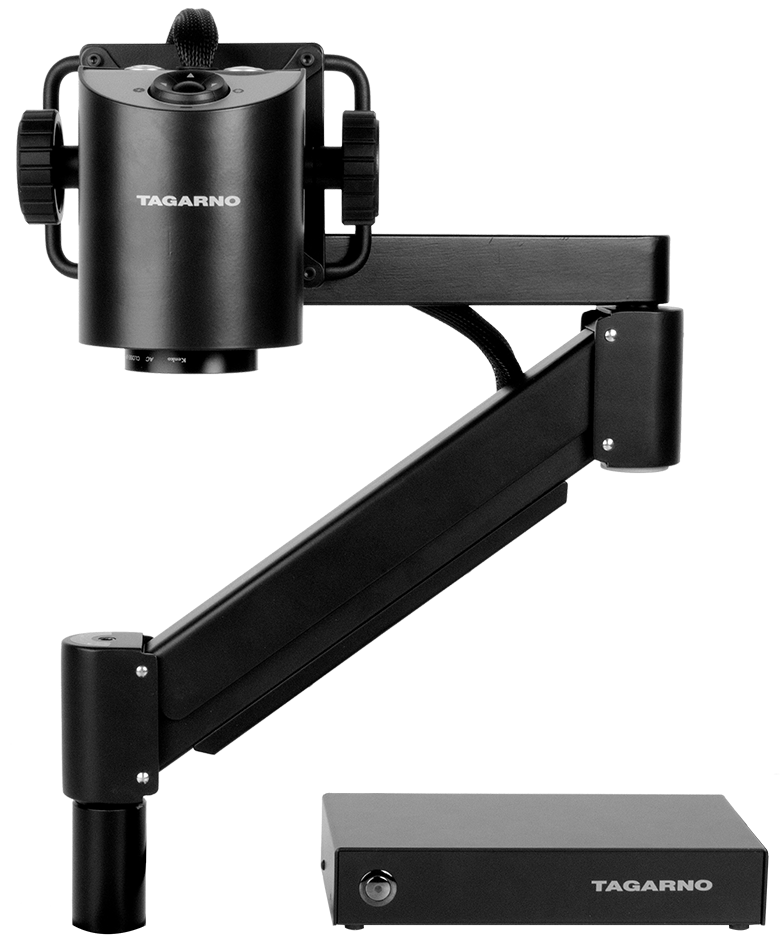
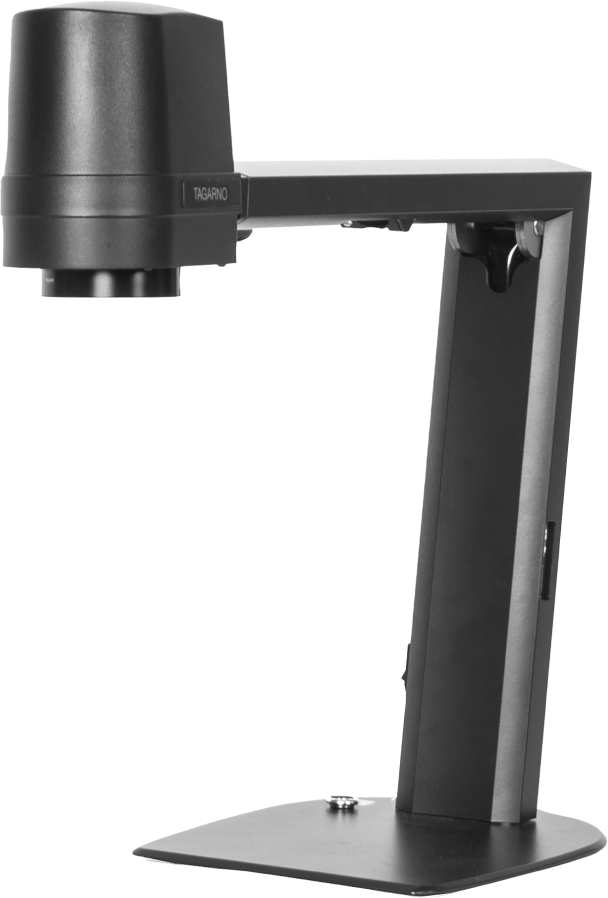
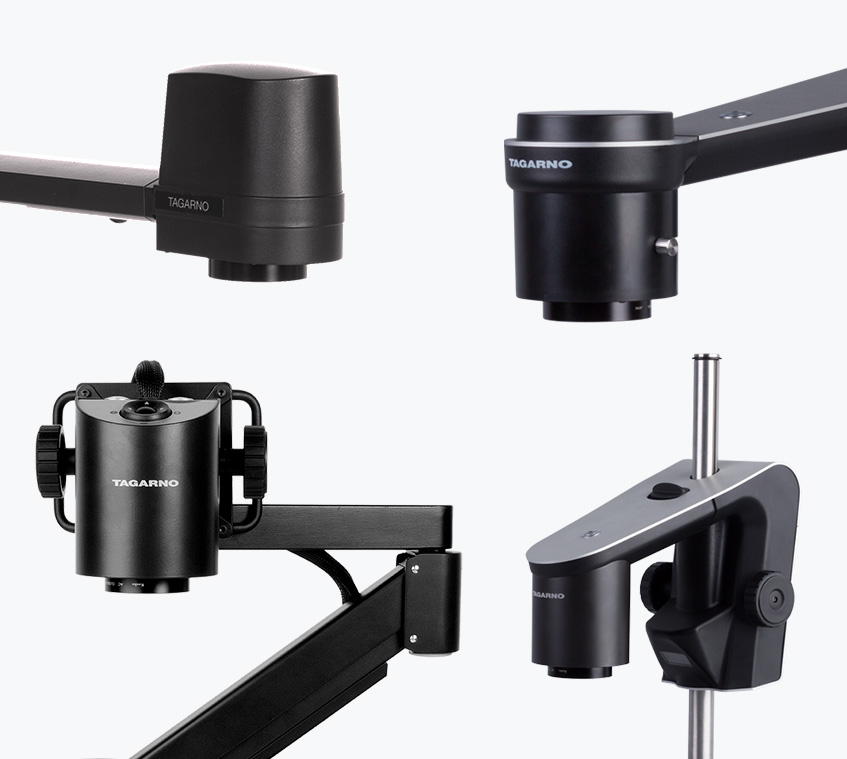
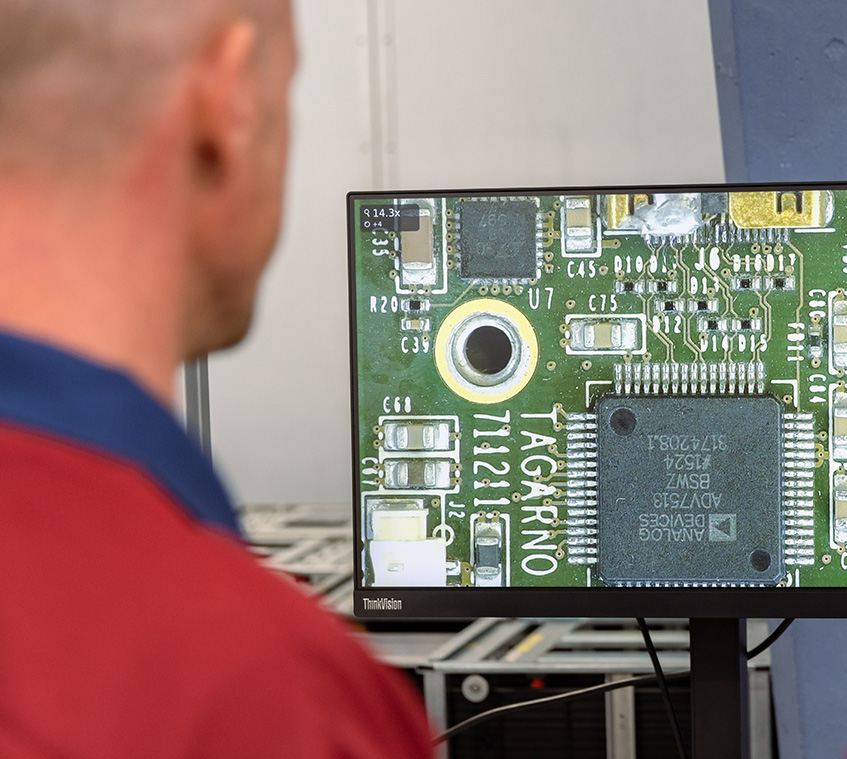
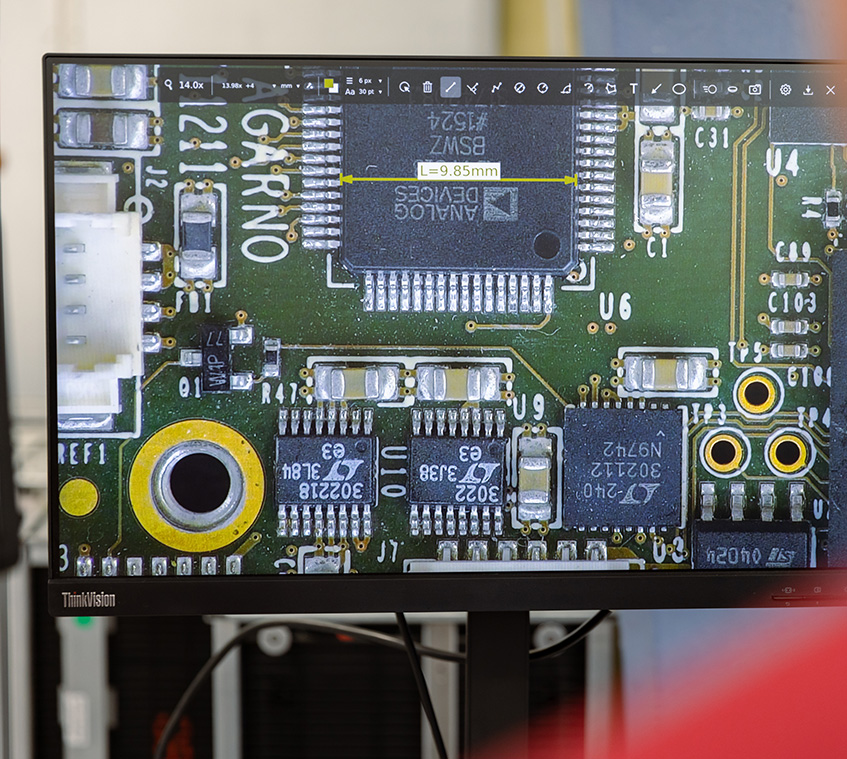
Compound microscopes with Transmitted or Reflected light
Although compound microscopes are available in two different versions, both are characterized by their eyepiece and their primary magnification being via objectives and secondary magnification via an eyepiece, usually 10x.
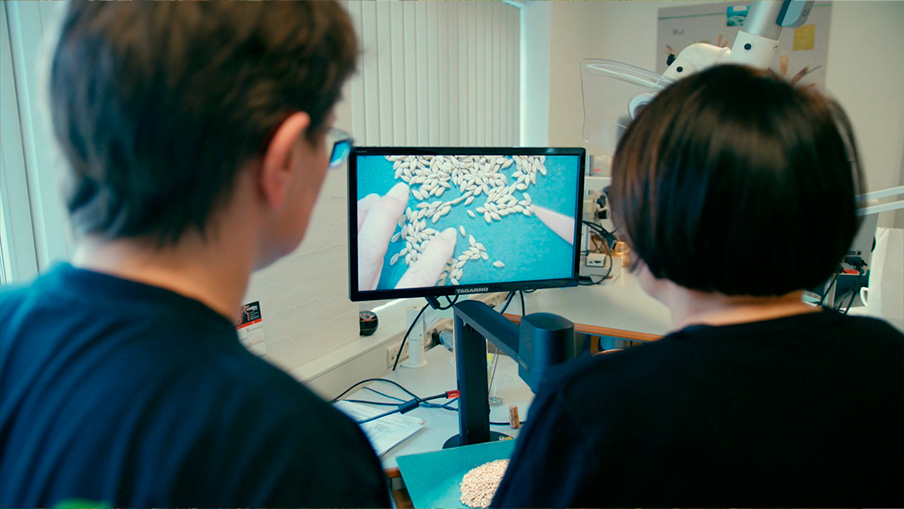
Where the compound microscopes varieties differ however is in terms of light source. With Transmitted light compound microscopes, the sub-stage illumination lights the samples from below, allowing light to transmit through the sample to the lens. Transmitted light compound microscopes can also structure or adapt the illumination system through their sub-stage condenser to provide greater contrast to samples that have none themselves. These microscopes are typically used in biological applications to inspect blood cells, parasites, bacteria, and various kinds of tissue.
If the sample itself is not transparent and requires light illumination from the top to reflect from the sample, a Reflected light compound microscope is used. Examples of applications for the Reflected light compound microscope include metal failure analysis, wafer inspection and anything where light can’t pass through.
When choosing a microscope, it’s important to know that compound microscopes use two lenses to create a two-dimensional image and can typically provide higher magnification levels than stereo or other low power microscopes.